Content
Likewise, a portable piece of equipment used by a construction company would be a fixed asset, even though it is not technically affixed to any structure. The energetic modernisation or replacement of existing equipment can be greatly assisted by the adding of depreciation allowances; and the existing allowances on depreciable assets cannot fail to be inadequate. Another factor to consider is that large asset purchases are often financed with borrowed capital. When that is the case, the initial exchange of cash and asset book value is smaller than an outright purchase . As loan principal payments are made, cash is exchanged for an increased portion of the asset book value that in turn increases the equity or owned portion of the asset.
- Some other systems have similar first year or accelerated allowances.
- This method of depreciation allows a larger tax deduction in the early years of an asset and less in later years.
- A capitalization limit may also be applied to keep lower-cost purchases from being classified as depreciable assets.
- You can also depreciate some forms ofintangible property like patents, copyrights, and computer software.
- Businesses depreciate long-term assets for both accounting and tax purposes.
Straight-line depreciation generates a constant expense each year, while accelerated depreciation front-loads the expense in the early years. Some companies choose the accelerated method to shield more income from tax, though their reported net profits will be less in earlier years. This will reverse in the later years, as less depreciation expense is recorded. When preparing the balance sheet, be careful to only record the purchase price and keep it there until you dispose of it. Yes, you will be depreciating the value over time, but those transactions are also accounted for in order to accurately show profit. The balance sheet simply shows the value of the van at the time of purchase ($25,000). Now that we know that non-current depreciable assets are property, plant, and equipment, let’s discuss how we would go about purchasing these assets.
Objective of IAS 16
For 2018, changes to depreciation will take place, particularly tobonus depreciation. This change will allow businesses to deduct 100% of the cost of eligible property in the year it’s placed in service.
For example, a vehicle depreciates the second you drive it off the lot. Depreciation is spread out over the expected life of the asset, down to its salvage value, or how much you’ll get to scrap it. You are reducing the value of the asset, therefore reducing the overall cost of the asset and accurately showing the true profit earned from the asset.
IASB publishes proposed IFRS Taxonomy update
The cost of an asset is the total price to acquire an asset and make it ready for use. The types of 1231 property include depreciable property and real property (e.g. – buildings and equipment) used in a trade or business and held for more than one https://online-accounting.net/ year. You generally can’t deduct in one year the entire cost of property you acquired, produced, or improved and placed in service for use either in your trade or business or income-producing activity if the property is a capital expenditure.
If the company receives a $12,000 trade‐in allowance, a gain of $2,000 occurs. Volatility profiles based on trailing-three-year calculations of the standard deviation of service investment returns. Founded in Depreciable Asset Definition 1993 by brothers Tom and David Gardner, The Motley Fool helps millions of people attain financial freedom through our website, podcasts, books, newspaper column, radio show, and premium investing services.
Depreciation (cost and revaluation models)
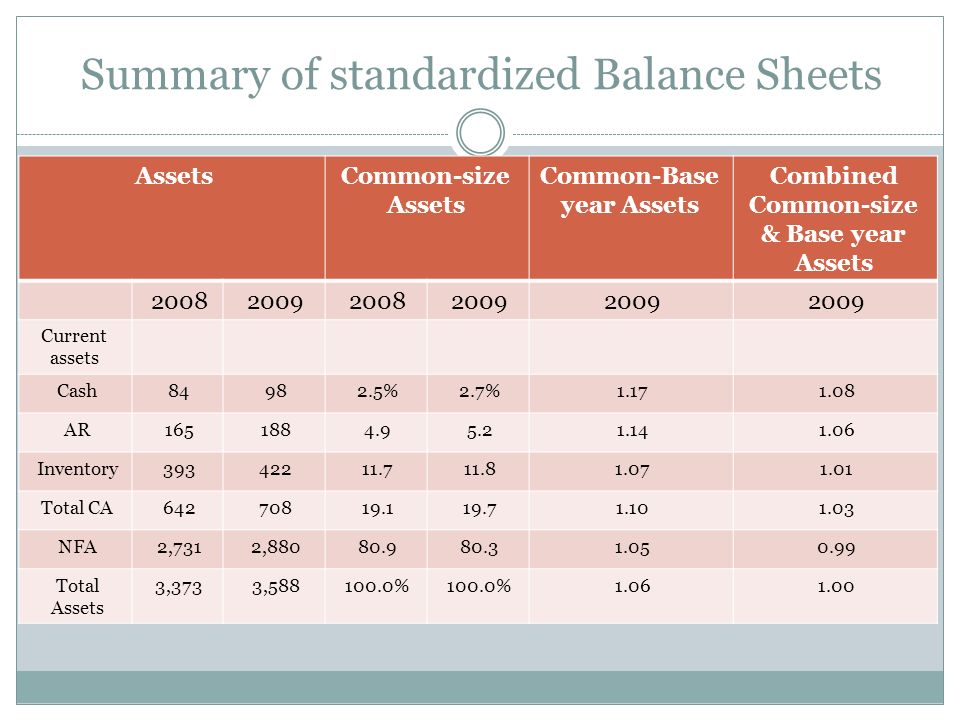
Other non-current assets can include investments, intellectual property, and brand recognition. You are starting a flower delivery business and need to purchase a delivery van. Before you go over to Al’s Vans and make a payment, there are a few things to consider from a business and accounting perspective. Purchasing a delivery van means you are purchasing a non-current depreciable asset. In this lesson, we will discuss non-current depreciable assets, how to purchase them, and how to enter the purchase in the general journal. Examples are provided to show how to assess the cost and the bookkeeping for the purchase of non-current assets.
- A non-current depreciable asset is expected to generate revenue for your business over its useful life, referred to as economic benefit.
- In addition, this gain above the depreciated value would be recognized as ordinary income by the tax office.
- Under such a convention, all property of a particular type is considered to have been acquired at the midpoint of the acquisition period.
- Depreciation is an accounting method that a business uses to account for the declining value of its assets.
- Useful life represents how long is likely to be profitable to the business.
However, in most countries the life is based on business experience, and the method may be chosen from one of several acceptable methods. And finally, if you improve depreciable property, that improvement, at least for tax purposes,should be treated as a separate depreciable property. This would occur if you make an addition or partial replacement to a property that adds to its value. If, on the other hand, you’re just repairing a property, you can typically deduct this as a business expense. According to the IRS, “The Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System is the proper depreciation method for most property”.
What is Tax Depreciation?
Other costs of assets consumed in providing services or conducting business are an expense reducing income in the period of consumption under the matching principle. One such rule, in effect from 2010 to 2013, allowed business owners to expense certain types of property in the first year of its useful life – up to a limit of $500,000.
What are the 3 types of assets?
- Current Assets. Current assets are assets that can be easily converted into cash and cash equivalents (typically within a year).
- Fixed or Non-Current Assets. Non-current assets are assets that cannot be easily and readily converted into cash and cash equivalents.